As you evolve into a world-class digital marketer, you need to take your SEO skills to the next level.
Search optimization has many facets and many levels of understanding. So, we have broken down advanced, high-level SEO topics into an easy-to-use and easy-to-implement guide.
What is SEO Strategy?
SEO strategy is a planning process used to optimize your website for search engines like Google. The goal is to increase rankings for specific keywords. Components of a good strategy include Technical SEO, On-page SEO, and Link Building.
Complete 3 Step SEO Strategy Blueprint
For those just starting out, let's start with a few basics and define SEO. First, SEO is an acronym for search engine optimization and a marketing process for increasing the volume of website traffic from search engines. SEO relates specifically to the increase of organic search results and excludes paid and direct traffic visitors.
To improve ranking factors, you must optimize your website using a comprehensive SEO Strategy Plan. I've outlined our 3-step Agency Blueprint for Search Engine Optimization below.
SEO Strategy Step 1: Technical SEO
You should build all SEO Strategies on a solid Technical SEO foundation. Often referred to as On-site SEO, this foundation refers to the website, hosting server, and DNS optimizations. These technical optimizations are vital in helping search engine crawlers index your site more effectively.
Learn SEO Tutorial: How HubSpot Uses Blogging to Rank #1 on Google
If you're building a "new website", check out SEO for a New Website.
SEO URL Structure
Your SEO URL, or “slug”, is important for search. For good practice, keep URLs short, using the target keywords most relevant to your web page topic.
SEO URL Tips:
- Use all lowercase
- Use only dashes (hyphens) to separate words
- Max of 512 characters or Google will truncate
- Limit using stop words: a, the, to, etc., where possible
Page Load Speed
Your site speed is extremely important to SEO and is now a ranking factor. Google considers a slow-loading site to be a poor user experience. There are many factors that can affect your website’s load time.
How to Improve Page Load Speed:
- Use a top hosting provider: WPEngine, HubSpot, etc
- Use a premium SSL certificate for HTTPS
- Change your DNS service to CloudFlare
- Serve optimized images
- Serve site files via a CDN
- Use server-side caching
- Run a weekly Technical SEO Audit
SEO Navigation Best Practices: Menu and site links
When search engine crawlers visit your web pages, they follow your links. As we mentioned, Google does a better job reading text. So, use text-based links for your website navigation and body links to improve the crawlability of your website.
Don’t underestimate the power of your links. They help the crawler discover new content. Strategic links can help the crawler determine the topic relevance of the link it follows and the relationship of the destination web page to the current page.
Tips for SEO Anchor Link:
- Use a keyword as your anchor text link instead of “click here”.
- Don’t over-saturate your pages with links. 1-2 links every few paragraphs.
- Too many links on your page could max out your crawl budget.
- Link to external sites when it helps add value and context for the user.
- When linking externally, give link preference to high authority sites.
- When linking externally, don’t use rel=”nofollow” in your anchor link.
- Link to internal pages when it helps add value and context to the user.
- Link internally when the destination page is topically related.
- Link internally when the linking page is part of a content cluster.
- When linking externally, give link preference to high authority sites.
- Don’t be afraid to use same-page anchor links.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a simple file that lives online alongside your website. It serves as a roadmap to your most important web pages, blog posts, and site assets.
XML sitemaps are good for SEO because they speed up the crawling of your content. This file makes sure Google can find all important pages besides helping it interpret your site’s structure. In addition, the acts as a failsafe if the crawler doesn’t discover every site link.
Robots.txt File
A robots.txt is a simple text file that lives online alongside your website. Its job is to give indexing instructions to the search engine crawlers. Each instruction will allow or block the crawler from indexing specific file paths.
Also, the robots.txt file is standard practice and used to prevent the crawler from indexing non-essential files, web pages and directories. It’s good for SEO and will improve the speed and effectiveness of each crawl.
Broken Links & Broken Redirects (404 not found error)
I’m sure you’ve seen it before: the HTTP 404 Not Found Error. It simply means you were trying to load a web page or file resource that couldn’t be found. It’s the result of a broken link or redirect.
A broken site link sends visitors to a non-existent resource. Not good.
A redirect is a server instruction - when "page A" is requested, load "page B" instead. A broken redirect also sends visitors to a non-existent resource.
Broken links and redirects happen when moving content or renaming page URLs, but don’t update your links. It happens to everyone. But it creates a poor user experience. In addition, it’s bad for SEO as the crawler can’t index non-existent content. A simple site audit or a trip to Google’s Search Console can help you discover these issues.
Duplicate Content
Duplicate Content is content that’s identical or very similar to other published content in multiple internet locations. Where locations are defined as unique URLs. The concern is that Google doesn’t always know which content to give preference. This confusion can cause poor ranking.
There are many myths about content duplication. One myth cautions that Google may penalize your content. I’m not here to challenge the myths, nor have I ever seen such a penalty. I will say that you aim for high-quality, unique content, and Google will reward you for it.
If you’re a guest blogger, you’ll know there are situations where your content will live in multiple locations. Whether you produce original content for another site, then republish on your site later, or vice versa, there’s a simple fix. Use the handy HTML rel=“canonical” Tag on each subsequent instance of content. It tells Google where the original version lives - everyone's happy.
SEO Meta Tags
SEO Meta Tags are bits of HTML code that live on every web page of your site. They offer more detail about your web page to the search engines and are very important to SEO.
Important Meta Tags for SEO
- Title tag
- Meta description tag
- Viewport tag
- Social meta tags
- Meta content-type tag
- Canonical tag
As a matter of good practice, you should stay away from using the keyword tag.
Structured Data Markup
Special bits of code (or Schema.org markup) are added to a web page's HTML that’s interpreted by search engines. Google will use this structured data to generate rich snippets inside their search results. Excellent for SEO as a featured snippet can outrank the top organic positions.
Mobile Optimization
Last but certainly not least. Mobile optimization is the practice that allows a website to adapt to smaller devices. In web development, it’s referred to as mobile responsive.
Older-style websites were once designed specifically for the desktop experience. When the bulk of search traffic shifted to higher mobile usage, users had to pinch and zoom to see content. Not a great experience. For a time, an organization might create a second mobile version of their site, i.e., https://m.mysite.com. Of course, you had to support multiple versions of the site.
Responsive websites overcome that challenge. The website and its content now “respond” to the device viewing it - desktop, smartphone, or tablet. The new mobile-optimized standard ensures a good user experience across all devices within any orientation.
In addition, a mobile-optimized website is good for SEO and is now a ranking signal. That's right, Mobile First Indexing Impacts SEO. As of March 2018, Google started its rollout of the Mobile-first index.
This means they’ll use the mobile version of your website for indexing and ranking.
SEO Strategy: Step 2
On-page SEO
On-page SEO (AKA on-page optimization) is a series of marketing tactics used at the website level to improve user experience and search positions. On-page tactics include content optimization, keyword optimization, mobile optimization, snippet optimization, etc.
It’s common practice to start your on-page efforts with keyword research. Not a bad place to start. You might base your keywords around your product names, services, or business type. But, this may yield broad terms with low search intent.
You need to know more about your audience and what problems, challenges, or needs they need to be solved. Who do you want to have a conversation with? Your ideal customer, right? Then, you need to develop a buyer persona first to find these factors. Once you do, you’ll have more useful data to fuel your keyword research.
What is a Buyer Persona?
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your ideal customer based on real customer data and market research. No guessing, please.
No SEO guide should be complete without a brief intro to the buyer persona. Do you know who your targeted consumer is?
Ideally, you’d want a blueprint of your ideal customer. You’d want to know their age, gender, and economic makeup per demographic. Moreover, you’d want to understand what drives them.
Every page of your website should speak to this consumer with targeted keywords aligned to their needs and challenges. Most importantly, you’d design your sales funnel for this buyer. Here’s an example:
Example Buyer Persona
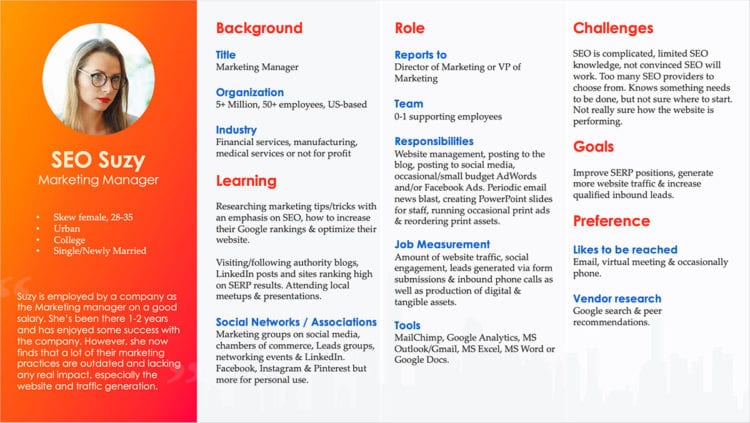
Let’s say Mary is your ideal customer. What problems do you need to solve for Mary? What topics or terms might she use in the search? Focus on the “Challenges” and “Goals” for starters.
Then, ask yourself, Do I offer a product or service that can help Mary with her challenges or goals?
Answering these questions will lead you closer to keyword opportunities that are better aligned with your ideal customer’s needs.
Next, you need to know what’s motivating your ideal customers' search queries - something we call search Intent.
What is Search Intent?
Search intent (AKA keyword intent) is why someone uses the search engine.
There are a few types of search intent queries:
- Navigational - we don’t mean Google Maps, but people searching for a specific website usually via a brand name query.
- Informational - people looking for info about a specific topic or have a specific question.
- Transactional - people searching and intending to buy something.
- Commercial research - people looking to make a future buying decision. What’s the best flat-screen TV? They need more convincing, so they research specs, ratings, and sales. Think of commercial intent as a hybrid of informational and transactional.
Buyer Intent Keywords
The terms people use in search will help determine their intent. People using terms like buy, sale, or discount are likely to purchase something. Where people using terms like how to or DIY are looking for information. Also, where people using terms like best or versus are likely comparing products or service providers for a future purchase.
How to do Keyword Research (BKA Search Analysis)
In a nutshell, keyword research is the SEO task needed to define the best words people are using in search engines. Keyword research should also be the vehicle to help align your web page topics to search queries.
As mentioned, simply dreaming up keywords, your product/services, or business type won’t be enough to help you rank. Even if you could rank for broad terms for “financial services”, would you really want to? The term is very broad, with no buyer persona alignment and no search intent.
Example - your client is a financial advisor
Keyword idea 1: financial advisor
- Broad term, low search intent, and not aligned with buyer persona
- 90,500 monthly searches, extremely high competition
- 1.28 billion total SERP results (massive)
- Mixed search results: Google ads, how to become one, definition of, local results, what do they do, news stories
- Many organic results are internet authorities: CNBC, Forbes, USNews, etc
- It would be tough to outrank authority listings
Keyword idea 2: can I cash out my 401k while still employed
- Niche term, high search intent, and aligned with buyer persona
- 1,000 monthly searches, medium/high competition
- 482k total SERP results (good)
- Organic results: mainly blog post content that are education-based
- Top-ranking content is thin and unengaging
- The top list is beatable
Assumptions: Someone needs money for something soon; I know our client provides this service and helps people in this situation. Competition is on the higher, but our client’s domain authority is high enough to offset. The content we’d be looking to outrank is weak and last dated 2 years ago.
NOTE: these are real assumptions concluded from an actual client campaign using the following:
Keyword foundation research
- intense client discovery
- buyer personas created
- competitor research
- SERP listings research
- defined client goals
- set inbound targets (so we could measure success)
- formulate primary topics + related (synonym) topics relevant to the business & aligned with persona challenges or goals
Keyword validation via SEMRush:
- Organic Research Tool
- Keyword Magic Tool (our secret weapon, BTW)
- Organic Traffic Insights
- Keyword Difficulty Tool
- Backlink Analytics Tool
Caveat: Keyword Research is a big project that could take you 1-2 weeks even with the best research tools. The purpose of the guide is to provide the high points and a few examples and get you in the right direction. Backlinko has a great keyword research guide to expand your learning.
Your ultimate goal is to optimize for keywords that will solve for the user. Otherwise, you might create content for questions no one's asking. Resulting in little or no search traffic. On the other hand, poor persona alignment will cause low visitor-to-lead conversion. So, finding the right questions will lead you to the best keyword opportunities.
Keyword Optimization
Next, you must find the ideal way to integrate the keywords into your website’s structure. It may seem obvious, but, we do this to establish a priority and purpose of our page/post to the search engine.
Put the keywords toward the beginning of a post title (if possible) and within the first paragraph of the content. More placement opportunities include the page URL, H1 title tag, meta title, meta description, image file names, and image ALT tags.
URL
Follow my SEO URL Structure direction. Just a reminder to add your keywords to your URL.
H1 Title Tag
Your H1 title is usually the primary heading that sits atop your body content. It’s good practice to include your primary keywords in the title.
H2 - H6 Title Tags
Including synonyms or words semantically related to your keywords in your subheading titles is good practice.
First Paragraph
I like to start the first sentence of the first paragraph with my primary keyword. It should sound natural and add value to the context. Introducing the keyword right away reinforces its importance to Google.
Meta Title
What’s important here is that your primary keyword is present. Again, it should be natural and contextually relevant. More importantly, it’s the blue link displayed in the SERP, so it needs to stand out. Refer to the Meta Tags section for more info.
Meta Description
Your Meta Description should support your primary keyword and claim made in your Meta Title. Again, it should be natural and contextually relevant. This is the ad copy displayed in the SERP, so it needs to stand out. Refer to the Meta Tags section for more info.
Image Filenames
It may seem trivial, but you need to put your primary and related keywords into your filenames. The search engine can’t interpret the image but “can” read the filename.
I.e. - my-amazing-keyword.jpg
Image Alt Tags
Short for “alternative” and is the text used in place of the image for screen readers. Its purpose is to help visually impaired visitors understand the context of a placed image. So, use your keywords to describe the image adequately and in detail.
I.e. - my-amazing-keyword.jpg
Image Alt Tags
Short for “alternative” and is the text used in place of the image for screen readers. Its purpose is to help visually impaired visitors understand the context of a placed image. So, use your keywords to describe the image adequately and in detail.
Image Title Tags
We never come across any concrete data supporting the image title tags’ SEO significance. When setting our Image Alt Tag, we copy this value over to the image title for good measure.
Semantic Keywords
Mentioned earlier and referring to words similar in meaning or share some relationship with your primary keyword. It allows you to mix in related meanings, as not everyone knows terms by the same name.
Simple example: financial planner and financial advisor. Often used interchangeably.
Compound example: social media
Do you mean Facebook or Twitter or something else? Or do you mean the content shared amongst people online? What if I added terms like hashtags, tweets, and 280 characters to my content?
Adding semantic words will improve the relevancy to Google by adding context to your page’s purpose.
Content Structure for Web Pages & Posts
Other On-page factors important for SEO include internal links, external links, length of content, content diversity, content reading level, and multimedia.
Content Length
Longer content - typically, blog posts typically rank better in search, especially when part of content marketing. Not because of its length but because the writer covers the content in greater detail. Note: if the top 3 search competitors average around, say, 1,200 words, I won’t write 600 (too little) words nor 3,000 (too much).
Content Diversity
It’s important to keep your content interesting. Be sure to keep short sentences, lots of white space, relevant visual images/graphics/screenshots/infographics, and bulleted lists.
Content Reading Level
Known as the Flesch Reading Ease Score, it refers to the reading difficulty of your text copy.
Strive for a reading ease score of 60-70 that’s good for web copy.
Score of 70 - 60 = School level of 8th & 9th grade
It is considered to be plain English and understood by 13 to 15-year-old students.
Internal Links
Internal links make crawling your site easier and show relationships between the pages, which emphasizes relevance to core topics, AKA pillar pages.
External Links
Add external links to relevant websites, which increases the search engine’s understanding of your page’s topic. Tip - It’s best to link out to authoritative sites that add value to the visitor.
Multimedia
You should adopt a multimedia approach to add value to your content. Use videos, podcast players, and SlideShares to keep users engaged on your page longer. As mentioned earlier, this is a good search signal.
SEO Strategy: Step 3
SEO Link Building
AKA Off-site SEO is arguably the biggest ranking signal Google uses to determine page rank. SEO link building is the process of earning or gaining links to your site.
Sites with more backlinks tell Google it’s a quality resource worth linking to and generally earns a higher ranking.
What is a Backlink?
Quite literally, a hyperlink from a third-party site to yours. Think of a backlink as a vote or citation in favor of your site content.
Backlink Quality
Your page rank is influenced by the site linking to you. The more authoritative the linking site, the more impactful the confidence vote. On the flip side, low-quality backlinks can affect you adversely.
Backlink Quality Factors
Website Authority
- Trust Flow (coined by Majestic) - determine trust by measuring quality
- Citation Flow (coined by Majestic) - link popularity
- Domain Rating (DR)
- URL Rating (UR)
Page Relevance
- Topical Trust Flow
- Content Check (qualitative)
Site Credibility
- Is the linking site HTTPS (no = lower quality)
- Referring Domains
- Organic Traffic (no site traffic = low quality)
- Spam Score (by Moz) - determines the risk of penalization
Link Building Strategies
Any SEO guide stresses the importance of link-building. But, some feel that building links is an SEO magic trick. I can assure you there’s no sorcery. Here are a few examples of how to build backlinks:
Influencer outreach
Reaching out to relevant, authoritative site owners and show your content is worth linking to. A few ideas might include:
- Your content may be valuable to their audience (think):
- Resource guides, videos & infographics
- Your content is better than the content they’re linking to now
- They discuss the products or services you offer
- Your blog post directly answers a question
- Your content is more expansive or offers a unique perspective
Editorial Links via Brand Mentions
Results from producing high-value content that influencers link to organically with no influence by you nor sponsoring the link.
Guest Posting
Share your expertise with others. Guest posting (AKA guest blogging) is writing an article that’s published on another site. Site owners will generally allow you to include backlinks within your article to your website’s relevant content. Moreover, you can add your biography to the blog post where you share your website URL.
One note here. Google seems to be tougher on these types of links. There are sites solely in existence for guest posting for sponsored placements - so watch out. We’ll still guest post if it’s a super authoritative site with a high trust flow.
Local Citation
A local citation is a listing of your business name, address, and phone number in a local directory. Local directories can be a great place to create a listing, which is often free. The listing will comprise your business profile, website link, and often your social profiles. The linking power from these sites may not carry the weight they once did, but it’s still a good resource if you’re just getting started.
Be visible in your local community. The local Chamber of Commerce and bbb.org can be a great place to create a business profile and post your website from a respected site.
Backlink Analysis
It’s important to analyze your own link profile for new and lost backlinks and the over-quality of the links.
In addition, you’ll want to conduct competitive backlink analysis at regular intervals. It’s good to know who's linking to your competitors and to keep an eye out for new linking opportunities.
See our list of SEO resources for great SEO Link Building Tools & Backlink Analysis Tools.
Backlink Outreach
“Earning” your links and performing “real outreach” to impact your SEO takes work. I won’t sugarcoat it. Gaining new backlinks is hard... really hard, and links from your friend's websites won’t cut it either. Unless, of course, your friends are Neil Patel or Rand Fishkin (top SEO influencers).
Your links need to be built naturally and from high-authority websites - no cheating!






